Calibration Invariant Imaging
Object Classification through Scattering Media
with Deep Learning
Guy Satat, Matthew Tancik, Otkrist Gupta, Barmak Heshmat, Ramesh Raskar
A method for classifying objects hidden behind a scattering layer with a neural network. Training on synthetic data with variations in calibration parameters allows the network to learn a model that doesn't require calibration during lab experiments.
Traditional techniques to see through scattering media rely on a physical model that needs to be precisely calibrated. Computationally overcoming the scattering relies heavily on accurately calibrated physical models. Thus, such systems are extremely sensitive to an precise and lengthy calibration process.
In this work we overcome this bottleneck by utilizing neural networks and their ability to learn models that are invariant to data transformation. In our case, the transformations are variations in the imaging system calibration parameters. To that end, we create a synthetic dataset that contains variations in all calibration parameters (we use a Monte Carlo forward model to render the measurements). The system is then tested on actual lab experiments without specific calibration or tuning.

Overview:
The suggested imaging framework is introduced below:
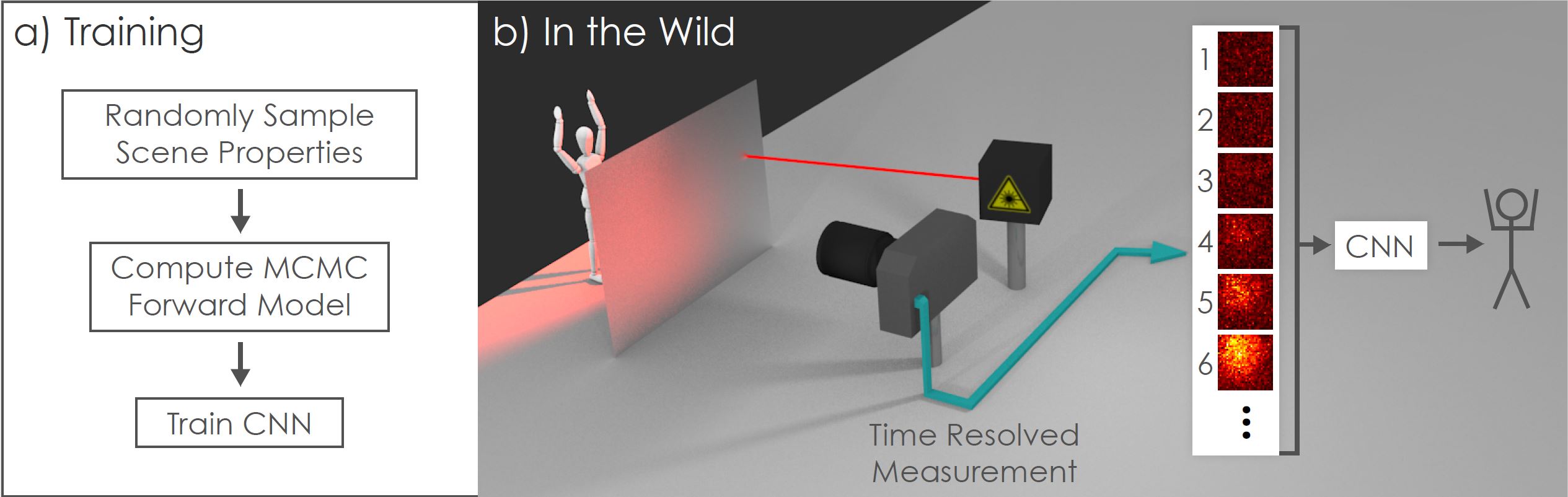
The first step is an offline process in which we render the synthetic dataset with a Monte Carlo based renderer and train the neural network.
The second step is the online imaging process. In this case we classify the pose of a mannequin hidden behind a paper sheet. The paper is illuminated by a pulsed laser, and a SPAD (Single Photon Avalanche Diode) camera captures a time resolved measurement of the reflected light. The data is fed into the neural network and the pose is classified.
Results:
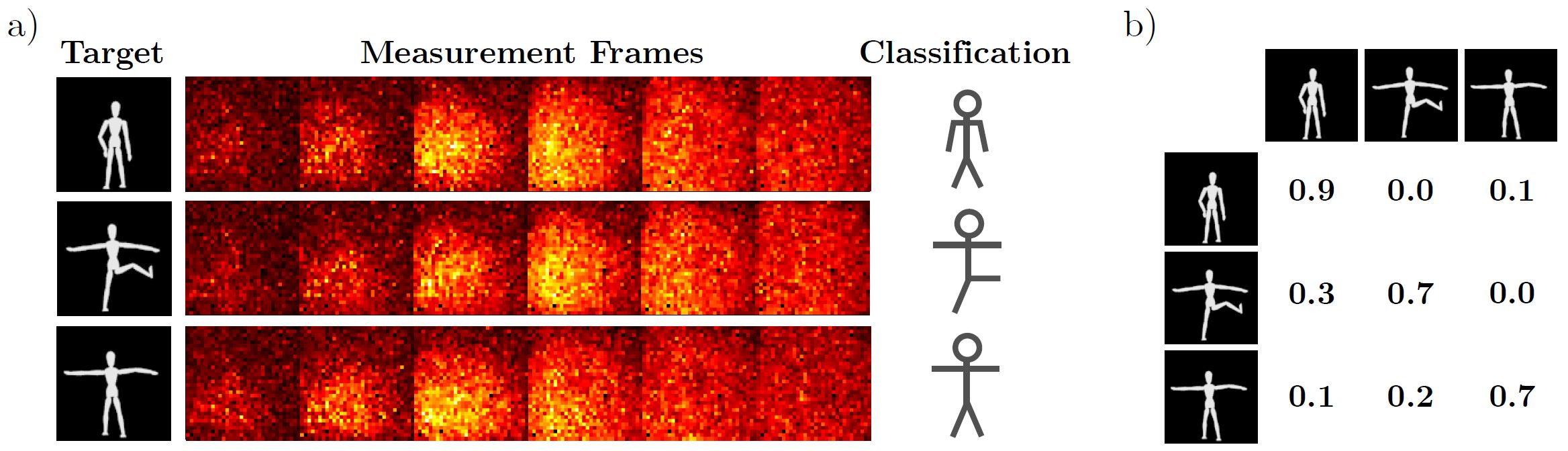
a) The three different poses and examples of the corresponding time resolved measurements.
b) The corresponding confusion matrix. The three poses are classified with 76.6% accuracy (compared to 33.3% random accuracy).
Paper Citation:
• G. Satat, M. Tancik, O. Gupta, B. Heshmat and R. Raskar, "Object Classification through Scattering Media with Deep Learning on Time Resolved Measurement", Optics Express Vol. 25, 17466-17479 (2017).
• doi: 10.1364/OE.25.017466.
• Local copy
Camera Culture Related Works :
• G. Satat, M. Tancik and R. Raskar, "Lensless Imaging with Compressive Ultrafast Sensing", IEEE Trans. Computational Imaging, (2017).
• G. Satat, B. Heshmat, D. Raviv and R. Raskar, “All Photons Imaging Through Volumetric Scattering”, Nature Scientific Reports, Vol. 6, 33946, (2016).
• A. R. Sanchez, B. Heshmat, A. Aghasi, M. Zhang, S. Naqvi, J. Romberg, R. Raskar, “Terahertz time-gated spectroscopic imaging for content extraction through layered structures,” Nature Communications, Vol. 7, 12665, (2016).
• B. Heshmat, I. H. Lee, R. Raskar, "Optical brush: Imaging through permuted probes," Nature Scientific Reports, Vol. 6, 20217, (2016).
• G. Satat, B. Heshmat, N. Naik, A. R. Sanchez and R. Raskar, "Advances in ultrafast optics and imaging applications," in SPIE 2016 (invited).
• G. Satat, B. Heshmat, C. Barsi, D. Raviv, O. Chen, M.G. Bawendi and R. Raskar, “Locating and Classifying Fluorescent Tags Behind Turbid Layers Non-Invasively Using Sparsity-Based Time-Resolved Inversion,” Nature Communications, Vol. 6, 6796 (2015).
• G. Gariepy, et al., "Single-photon sensitive light-in-fight imaging," Nature Communications, Vol. 6, 6021 (2015).
• B. Heshmat, G. Satat, C. Barsi, and R. Raskar, "Single-Shot Ultrafast Imaging Using Parallax-Free Alignment with a Tilted Lenslet Array," in CLEO: 2014 (oral).
• A. Velten, et al., "Recovering three-dimensional shape around a corner using ultrafast time-of-flight imaging," Nature communications, Vol. 3, 745 (2012).
• O. Gupta, et al., "Reconstruction of hidden 3D shapes using diffuse reflections," Optics Express, Vol. 20 (2012).
• A. Velten, et al., "Slow art with a trillion frames per second camera," ACM SIGGRAPH 2011 Talks ACM, (2011).
• R. Raskar, and D. James, "5d time-light transport matrix: What can we reason about scene properties," Int. Memo 7 (2008).
• N. Naik, et al., "Single view reflectance capture using multiplexed scattering and time-of-flight imaging," ACM Transactions on Graphics (ToG), Vol. 30. No. 6. ACM, (2011).
Related Talks:




